Intriguing evidence gleaned from the Martian surface suggests that the Red Planet may have once enjoyed a climate far removed from the arid, desolate landscape we see today. Recent analysis of peculiar “bleached” rocks, specifically fragments of bleached clay, points towards a past where Mars was a warm, wet, and potentially habitable oasis.
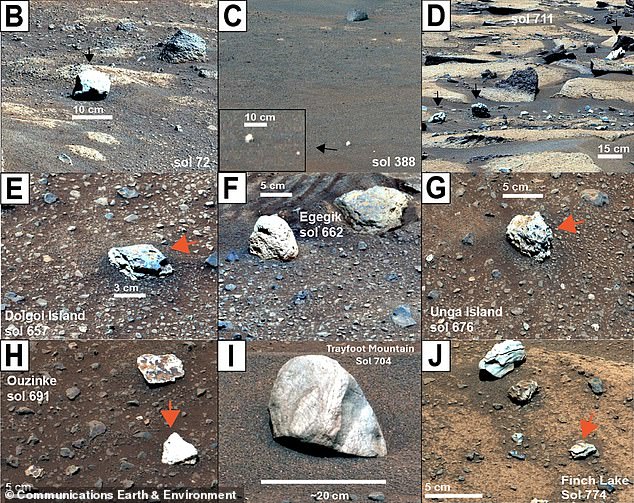
Researchers at Purdue University in Indiana have been meticulously examining images captured by NASA’s Perseverance rover. These images reveal fragments ranging in size from small pebbles to substantial boulders, all displaying a distinctive bleached appearance. The composition of these fragments, primarily the clay mineral kaolinite, strongly indicates the presence of liquid water and a humid, tropical-like climate that persisted for millions of years.
Professor Briony Horgan, a planetary scientist at Purdue University, emphasizes the significance of these findings, stating that these rocks are potentially some of the most crucial outcrops observed to date. The implications are profound, suggesting that Mars may have once resembled Earth’s tropical regions, such as the Amazon rainforest in South America or the Guinean Forests of West Africa. This discovery adds compelling weight to the growing body of evidence suggesting that Mars once possessed the necessary conditions to support life.
The Jezero Crater Connection
The location of these intriguing rocks is also significant. They were discovered within the Jezero Crater, a vast 28-mile-wide impact basin that scientists believe once held a substantial body of liquid water billions of years ago. The Perseverance rover, equipped with sophisticated instruments like SuperCam and Mastcam-Z, has been instrumental in analyzing the composition of these fragments.
The analysis has revealed that the fragments are largely composed of kaolinite, a white clay mineral that typically forms under tropical conditions on Earth. The formation of kaolinite requires prolonged exposure to a wet, rainy climate, where rocks and sediment are leached of other minerals over millions of years. The presence of kaolinite on Mars, therefore, strongly suggests that the planet once experienced similar conditions – humid environments with considerable rainfall.
Implications for Habitability
Professor Horgan highlights the implications of these findings for the potential habitability of Mars in the distant past. “The evidence in these rocks really points toward these kinds of ancient warmer and wetter environments,” she explains. “When we think about the possibility of these rocks on Mars representing a rainfall-driven environment, that is a really incredible, habitable place where life could have thrived if it were ever on Mars.”
The puzzle remains, however, as to the origin and distribution of these kaolinite fragments. There is no major kaolinite formation in the immediate vicinity of where the fragments were found, raising questions about how they arrived at their current location.
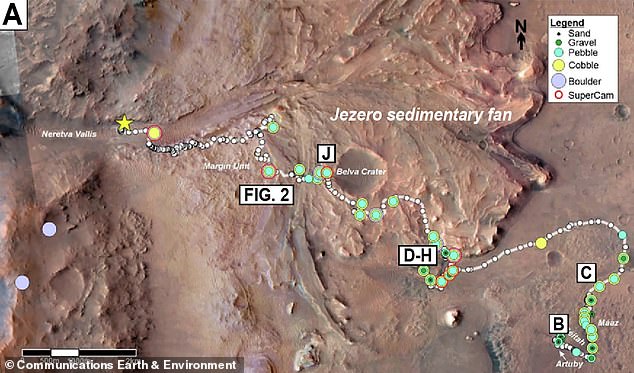

Possible explanations include:
- Transportation by ancient rivers: The fragments may have been washed into Jezero’s lake by the river that once fed the delta within the crater.
- Impact event: The fragments could have been ejected into Jezero by an impact event and subsequently scattered across the area.
The fact that such rocks are so difficult to form, requiring vast amounts of water, presents a stark contrast to the Mars we know today.
The Modern Martian Environment
Today, Mars is a far cry from the potentially lush environment suggested by the kaolinite fragments. It is a dry, dusty, cold, and desert-like world with a very thin atmosphere composed primarily of carbon dioxide (around 95%). While water does exist on Mars, it is primarily in the form of water-ice locked beneath the surface in the polar regions. There is also a small amount of water vapor in the Martian atmosphere. Furthermore, some briny water seasonally flows down hillsides and crater walls. On Earth, ice is usually just frozen H2O. But on Mars, it’s actually water ice and CO2 ice mixed with each other. It’s so cold on Mars that it gets frozen, so you actually have those mixed together both at the poles and underneath the surface as well.
Despite the current conditions, the scientific consensus is that liquid water was once far more abundant on Mars, potentially transforming the planet into a world with blue oceans and verdant landscapes, much like Earth.
A History of Water on Mars
NASA estimates that approximately 4.3 billion years ago, Mars possessed enough water to cover its entire surface in a liquid layer about 450 feet (137 meters) deep. By 3.5 billion years ago, this water had become scarcer, channeled around the planet between crater lakes via rivers, similar to the river systems found on Earth.
Liquid water may have persisted on Mars as recently as 2 billion years ago, before the Martian atmosphere was significantly depleted and the remaining liquid water evaporated.
NASA summarizes the evidence for a watery past on Mars: “Mars appears to have had a watery past, with ancient river valley networks, deltas, and lakebeds, as well as rocks and minerals on the surface that could only have formed in liquid water. Some features suggest that Mars experienced huge floods about 3.5 billion years ago.”
The discovery of these bleached kaolinite fragments in the Jezero Crater provides further support for this view, offering a tantalizing glimpse into a past where Mars may have been a habitable world.